What is Stakeholder Management? | The 5 steps of Stakeholder Management


The success or failure of most projects can often be attributed to the lack of attention given to the interests and demands of stakeholders. These key players have the power to make or break a project, which is why it is essential to have a solid plan in place to identify their needs and effectively communicate with them.
Stakeholder management should be a crucial element of any project planning effort. By understanding and addressing the concerns and expectations of those who have a vested interest in the project, organizations can increase the likelihood of project success.
Stakeholder management involves identifying and analyzing individuals or entities who have an interest in or are impacted by your project and its outcomes. These stakeholders can be internal or external, such as members of the project team, project sponsors, executives, customers, suppliers, partners, and government entities.
The process of stakeholder management revolves around managing the expectations and demands of these stakeholders. It entails systematically planning to communicate with and engage stakeholders, ensuring their needs and concerns are addressed throughout the project lifecycle.
By proactively involving stakeholders, organizations can build positive relationships, foster collaboration, mitigate risks, and enhance project outcomes. Effective stakeholder management minimizes conflicts, maximizes support, and ultimately increases the chances of project success.
Taking the time to identify, analyze, and actively engage stakeholders through the stakeholder management process is crucial for project managers and organizations aiming to achieve their project goals while maintaining strong relationships with those affected by their projects.
Stakeholder management plays a crucial role in project success. It involves identifying, analyzing, and engaging individuals or entities who have an interest in or are impacted by a project and its outcomes. Whether internal or external, stakeholders such as project team members, sponsors, customers, partners, and government entities need to be effectively managed to ensure project success.
Effective stakeholder management allows project managers to proactively identify and address stakeholders’ needs and concerns. By engaging stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle, potential risks and issues can be addressed in a timely manner. This helps in minimizing conflicts, ensuring smooth implementation, and avoiding costly delays.
Engaging stakeholders in a meaningful way fosters positive relationships. When stakeholders feel heard and valued, they are more likely to provide the necessary support and collaboration. Positive relationships can lead to increased stakeholder satisfaction, support, and trust in the project team, creating a conducive environment for successful project delivery.
Involving stakeholders in the decision-making process can lead to more informed and effective choices. Their insights, expertise, and perspectives can contribute valuable input that may otherwise be overlooked. By considering a diverse range of opinions, project managers can make well-rounded decisions that align with stakeholder expectations and project objectives.
Stakeholders who are actively engaged are more likely to support the project and contribute to its success. By consistently communicating project updates, involving stakeholders in relevant discussions, and addressing their concerns, project managers can cultivate a sense of ownership and commitment among stakeholders. This ultimately leads to a higher level of participation, cooperation, and support.
Stakeholder management ensures that project goals align with stakeholder needs. By understanding stakeholders’ interests, requirements, and expectations, project managers can tailor project strategies and deliverables accordingly. This alignment not only satisfies stakeholders but also increases the likelihood of achieving project goals and objectives.
Stakeholder analysis helps project managers figure out who is involved or interested in their project. It allows them to understand what these people or groups want from the project and how it might affect them. By knowing who these important stakeholders are, project managers can communicate better with them, meet their expectations, address their concerns, and build good relationships. Stakeholder analysis also helps project managers predict any risks, handle conflicts, and get support needed for the project to be successful. In the end, it helps project managers make sure that the project’s goals match what the stakeholders want, encouraging teamwork and increasing the chances of achieving those goals.
Stakeholder management is essential for navigating internal, external, and societal contexts. By effectively managing stakeholders, organizations can gain support, create positive relationships, and achieve long-term success while considering the diverse interests and needs of those involved.
Internally, stakeholder management is utilized within your own organization. This includes managing changes in workflows such as implementing new collaboration methods or digitalizing systems. When initiating internal changes, it is essential to gain the support of managers and employees. The success of the change depends on their buy-in, making it strategically important to be a strong team player. As a product owner, scrum master, or change manager, you will often encounter this situation.
Stakeholder management can also be applied outside of your organization, especially in cases such as mergers and acquisitions. In these scenarios, it is crucial to consider not only internal stakeholders but also external stakeholders. They have a significant influence on the organization’s license to operate and market position. Generating support for the new partnership and maintaining a powerful market position becomes paramount.
Stakeholder management also plays a significant role within government entities. In the process of developing new policies, engaging societal stakeholders becomes important. They provide advice on laws and regulations that contribute to a sustainable future for humans and animals. A good example is Shell, which must balance the interests of shareholders with those of political and societal stakeholders advocating for sustainability. Collaborating with various experts in such situations enables visible success to be achieved.
Stakeholder identification is a crucial step in project management as it helps understand individuals or groups that may influence or be affected by the project. By identifying stakeholders and understanding their interests, project managers can effectively engage and manage these key players throughout the project lifecycle. There are several methods that can be utilized to identify stakeholders, including mind maps, SWOT analyses, and stakeholder salience models.
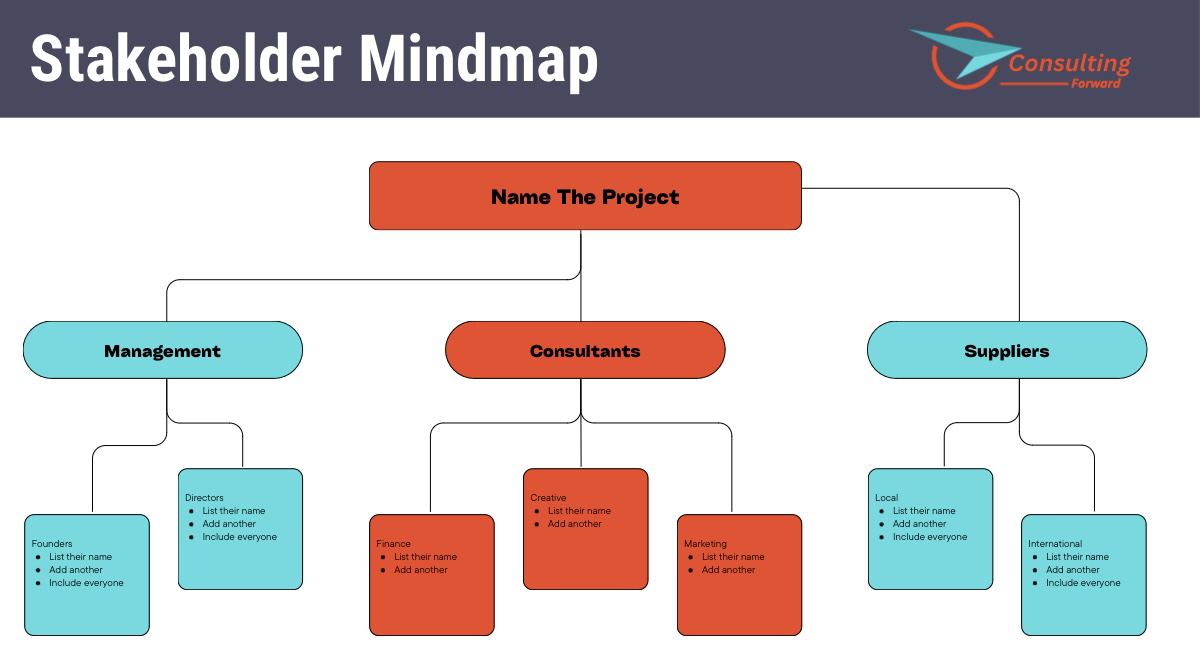
A mind map is a visual tool that helps organize information and uncover connections between various stakeholders. To create a mind map for stakeholder identification, start by placing the project at the center of the map. Then, draw branches to represent different categories such as internal stakeholders (e.g., employees, shareholders) and external stakeholders (e.g., customers, suppliers, community).
Next, add sub-branches to reflect specific stakeholder groups within each category. For example, under the internal stakeholders branch, sub-branches could include departments such as marketing, operations, and finance. With each stakeholder group identified, consider their interests, needs, and potential impacts on the project. The mind map allows for a visual representation of the stakeholder landscape, enabling project managers to better prioritize and engage stakeholders based on their influence and level of interest.
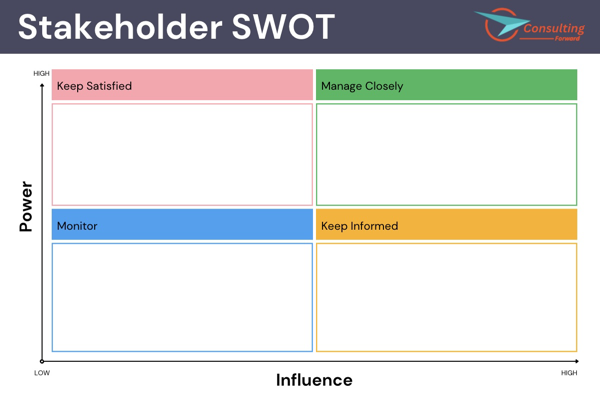
A SWOT analysis is another effective tool for stakeholder identification. SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Start by creating a table with four columns representing each element of the SWOT analysis. Then, brainstorm and list stakeholders under each column based on their perceived strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats they pose to the project.
By analyzing stakeholders in this format, project managers can identify key individuals or groups that may have significant influence on the project’s success. The SWOT analysis also allows project managers to consider stakeholder interests and concerns, enabling the development of appropriate strategies for engagement and management.
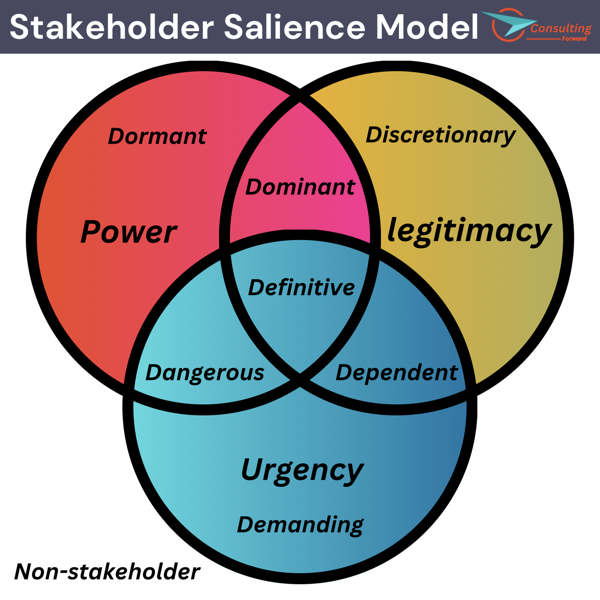
A stakeholder salience model helps project managers analyze stakeholders based on their power, legitimacy, and urgency. Power refers to the ability to influence project outcomes, legitimacy relates to the stakeholders’ relationship to the project, and urgency reflects the priority or immediacy of their concerns. By evaluating stakeholders along these dimensions, project managers can determine their level of salience or importance to the project.
The stakeholder salience model classifies stakeholders into three categories: latent, expectant, and definitive. Latent stakeholders have low power, legitimacy, and urgency and may not require immediate attention. Expectant stakeholders possess either power, legitimacy, or urgency and should be monitored and engaged accordingly. Definitive stakeholders exhibit high levels of power, legitimacy, and urgency and require active involvement in project decision-making and planning.
By using the stakeholder salience model, project managers can effectively allocate resources and tailor communication strategies based on the varying needs and interests of stakeholders, ensuring their influential voices are heard during the project’s execution.
When it comes to stakeholder management, one crucial aspect is determining the frequency of communication based on the stakeholders’ level of influence. By assessing the degree of influence each stakeholder holds, we can effectively design a communication management plan.
For stakeholders with high influence, it is recommended to have more frequent contact, such as bi-weekly meetings, to keep them informed and address any concerns they may have. Stakeholders with moderate influence may require monthly updates, ensuring they remain engaged and their interests are taken into account. Those with lower influence may only need quarterly communication to stay updated and maintain their interest in the project.
In stakeholder management, it is crucial to allocate a responsible individual for maintaining relationships with each stakeholder. This role can be assigned to the project manager, a member of the project management team, or someone from the steering committee. It is important to make the assignment based on seniority perspective and any existing relationships or location. As a general rule, avoid assigning more than fifteen stakeholders to a single person. By establishing these clear relationships, stakeholders can be effectively influenced and engaged throughout the project.
To ensure that the stakeholder representatives have a clear understanding of your expectations, it is crucial to prioritize listening and understanding. Effective communication goes beyond simply transmitting information about the project’s status; it also involves actively listening to stakeholders. Ask yourself the following questions: What knowledge do the stakeholders already possess about the project? How do they feel about the proposed changes?
By considering these questions, you can communicate more effectively and foster strong collaboration with both your team and stakeholders. It is essential to not only deliver the right information to stakeholders but also gather the necessary insights from them. Effective communication is the key to successful project execution.
Regularly discussing the outcomes of interactions with stakeholder representatives is a crucial step in ensuring alignment, information sharing, and a collaborative working relationship. This allows for adjustments to be made, ensuring that the expectations of both the project team and stakeholders are met.
Regular discussions also provide an opportunity for the team manager to address concerns, questions, or issues raised by stakeholders, promoting transparency, trust, and rapport. By evaluating progress and making necessary adjustments, effective communication and understanding can be maintained, enabling the project to proceed smoothly with all parties working towards the same goal.
– This question is important for stakeholder management as it assesses a candidate’s understanding of identifying and prioritizing key stakeholders, which is crucial for effective engagement and communication.
– This question is a good interview question for stakeholder management as it evaluates the candidate’s methodology for identifying and prioritizing stakeholders, ensuring that their needs and expectations are properly addressed.
– This question helps assess the candidate’s ability to navigate and resolve conflicts between stakeholders, demonstrating their skills in managing stakeholder relationships and maintaining project alignment.
– This question allows the candidate to showcase their communication skills and strategies specific to stakeholder management, ensuring clear and effective communication throughout the project lifecycle.
– This question helps evaluate the candidate’s ability to understand and assess the diverse needs and requirements of different stakeholder groups, informing their decision-making process in stakeholder management.
– This question assesses the candidate’s ability to influence and gain support from stakeholders, showcasing their skills in stakeholder engagement and persuasion.
– This question evaluates the candidate’s risk management abilities in stakeholder management, ensuring proactive identification and mitigation of potential risks that may affect stakeholder relationships.
– This question helps assess the candidate’s approach to involving stakeholders in decision-making, ensuring their active engagement and participation in shaping project outcomes.
– This question allows the candidate to demonstrate their strategies and practices for maintaining stakeholder satisfaction and engagement, ensuring that their needs and expectations are continuously met throughout the project.
– This question is a good interview question for stakeholder management as it allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to handle challenging stakeholder relationships and showcase their conflict resolution skills.
– This question helps assess a candidate’s ability to manage competing needs and interests of different stakeholders, which is crucial in stakeholder management.
– This question evaluates a candidate’s ability to navigate conflicting stakeholder perspectives and find solutions that align with the overall project objectives.
– This question allows the candidate to showcase their ability to influence stakeholders and gain their support, which is essential for successful stakeholder management.
– Communication plays a vital role in stakeholder management, and this question allows the candidate to explain their preferred communication approach and demonstrate their ability to effectively engage with stakeholders.
– This question assesses the candidate’s organizational skills, which are crucial in managing and coordinating information, interactions, and expectations with multiple stakeholders.
– This question helps evaluate the candidate’s ability to discern and prioritize relevant information for different stakeholders, ensuring effective and targeted communication.
– This question assesses the candidate’s strategies for collecting valuable feedback from stakeholders, indicating their commitment to understanding stakeholders’ needs and expectations.
– This question allows the candidate to showcase their ability to build trust and establish effective working relationships with stakeholders, which is crucial for successful stakeholder management.